Username
Password
Not a member? Register now
Name
Username
Password
Already a member? Sign In
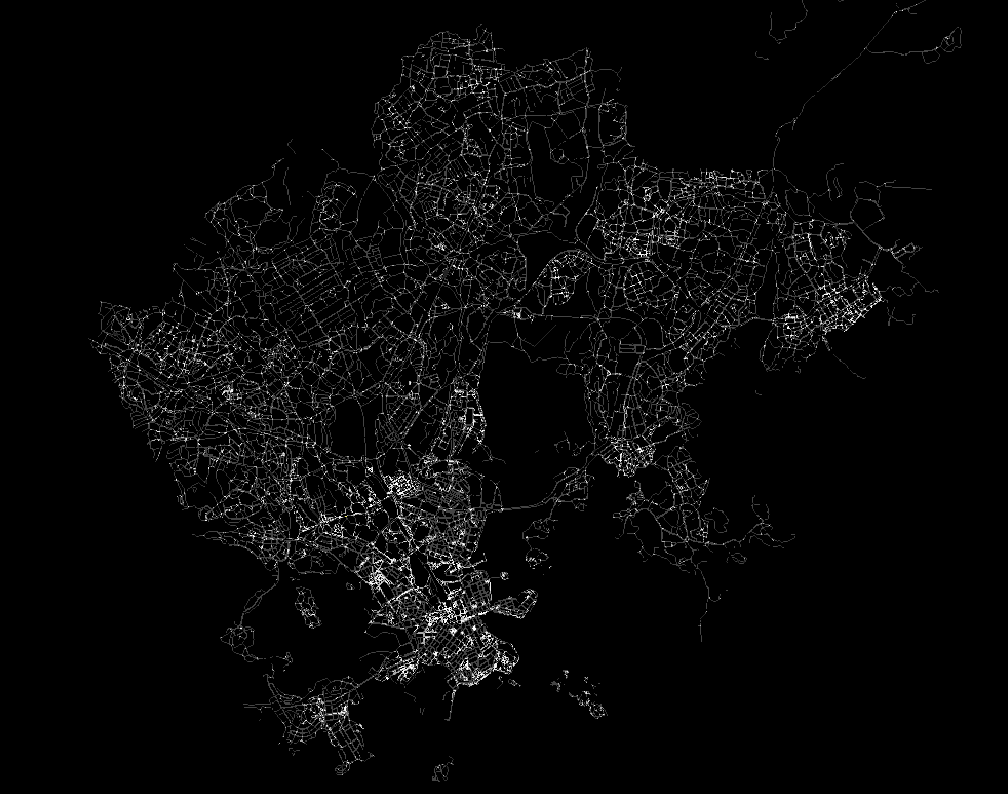

Connectivity of Street Network calculated through Space Syntax in Helsinki (Base map: Helsinki Open Data Service; The figure: made by author)
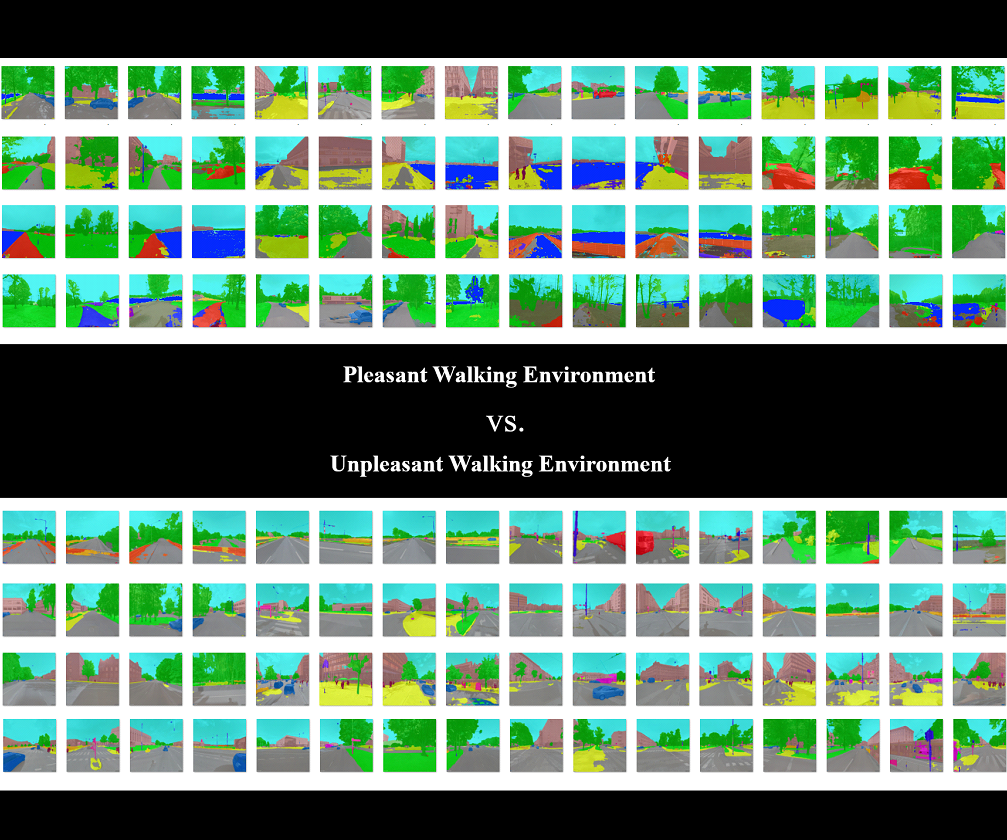
Extracting features of the street environment through Google Street API and deep learning model (made by author) to determine which kind of features affect the walking environment
Cities face increasing urban challenges and the factors affecting urban development are typically complex. Walkability is chosen as an entry point of the research since it represents urban complexity and sustainability. While walkable neighbourhoods deliver substantial benefits in terms of health, air quality, and sustainability, current walkability assessments suffer from technical challenges. Map-based methods fail to measure the details on a street level and observation-based studies fall into subjective dispute.
The long-term goal of the research is to find how machine learning and deep learning facilitate urban planning in respect of extracting and analysing data and predicting human-centred urban states in the coming future to react effectively and swiftly to urban challenges and complexity. The short-term goal seeks an innovative approach to overcome the current technical challenges of walkability assessment in urban planning.
Through the utility of urban digitization, big data and artificial intelligence, a smart system is constructed to predict walkability on different levels and provide quantifiable advice. The study focuses on transforming intangible data into tangible data in urban state prediction. Meanwhile, it tests how machine learning and deep learning can be employed in urban data analysis and evaluation through automatic learning. With this approach applied to other similar aspects in urban planning, the transformation of urban evaluation will speed up from conventional assessment into AI-based prediction, so cities can cope with the complex factors in urban planning efficiently and timely.
“From intuition to reasoning: analyzing correlative attributes of walkability in urban environments with machine learning”
Authors: Jun Yang, Pia Fricker, Alexander Jung
in Buhmann/Ervin/Palmer/Tomlin/Pietsch (Eds.): JoDLA 2022 – Journal of Digital Landscape Architecture – issue 7-2022, to be published in May 2022
Author
Jun Yang
Thesis Supervisor
Pia Fricker
Thesis Advisor(s)
Alexander Jung and Anssi Joutsiniemi
Start Year
2020 -
Keywords
Walkability, Evaluation, AI, Big Data